Decimals are a way of representing numbers using a base-10 system, where each digit represents a power of 10. This mathematical concept is essential for performing calculations and solving mathematical problems involving fractions and real numbers. Understanding decimals enables us to represent values precisely, manipulate numbers effectively, and apply mathematical principles to real-world scenarios.
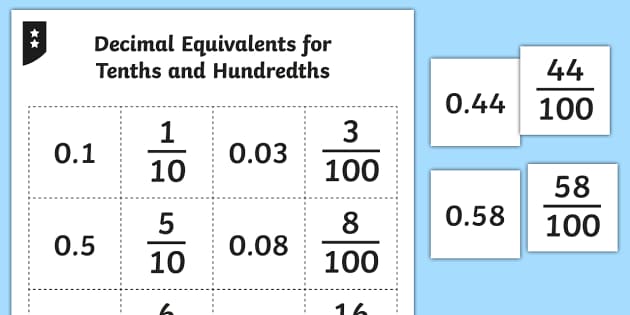
Image: www.twinkl.co.cr
Converting Fractions to Decimals: A Step-by-Step Guide
Converting a fraction to a decimal involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. This process yields a decimal expression that represents the same value as the fraction. For instance, converting the fraction 1 by 50 to a decimal involves division: 1 ÷ 50 = 0.02. Therefore, the decimal representation of 1 by 50 is 0.02, indicating 2 hundredths.
Decimal Applications in Measurement and Currency
Decimals have myriad applications in our daily lives. One common use of decimals is in measurements. For example, when measuring distance, we often use decimals to represent values smaller than one meter, such as centimeters and millimeters. Decimals also play a critical role in currency, enabling us to represent monetary values with fractional components. By using decimals, we can express precise amounts and perform calculations involving money accurately.
Decimal Operations: Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, and Division
Performing basic arithmetic operations on decimals follows similar rules as for whole numbers. However, some minor adjustments are necessary to account for the decimal point. For addition and subtraction, we align the decimal points vertically to ensure proper alignment of digits and avoid errors. For multiplication, we multiply as usual and place the decimal point in the answer to reflect the sum of decimal places in the factors. Division involves setting up a long division problem and paying attention to the placement of the decimal point in the quotient.
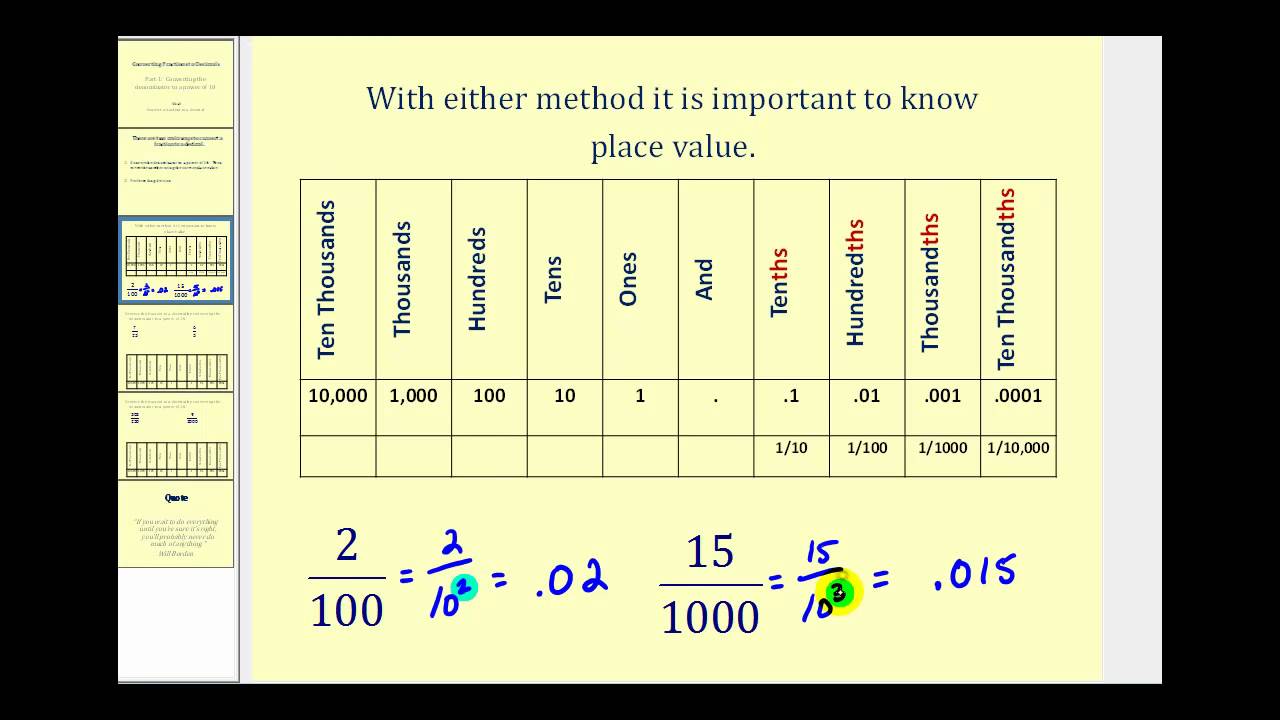
Image: www.youtube.com
Decimals in Science and Engineering
Decimals are widely used in scientific and engineering fields to express measurements, calculations, and data. Scientists rely on decimals to represent precise values of physical quantities, such as temperature, time, and distance. Engineers use decimals in calculations related to design, construction, and testing of systems, where accurate measurements and computations are crucial for achieving desired outcomes.
Importance of Decimals in Computer Science and Technology
Decimals also hold significant importance in computer science and technology. In computing systems, data is often represented using a base-2 number system (binary), but decimals are still used to represent fractional values and facilitate data exchange between different systems. Decimals are also crucial for specifying numeric precision in programming languages, where they define the level of accuracy required for calculations.
Write 1 50 As A Decimal Number.
Conclusion
Decimals are a fundamental concept in mathematics, serving as a versatile and efficient way to represent numbers. By understanding how to work with decimals, we can effectively perform calculations, solve mathematical problems, and apply our knowledge in various fields. From measuring distances to calculating monetary values and solving scientific equations, decimals empower us with a powerful mathematical tool that unlocks a world of numerical possibilities.

