Introduction:
When it comes to animal research, mice reign supreme as the most widely utilized species. Their small size, ease of breeding, and availability make them ideal candidates for a myriad of studies ranging from drug discovery to disease modeling. Let’s delve into the fascinating realm of lab mice and uncover the remarkable contributions they have made to medical advancements and scientific understanding.

Image: faunalytics.org
Mice: A Versatile Model Organism
The mouse’s humble beginnings can be traced back to the early 1900s, when geneticist Clarence Little began selective breeding experiments to study inheritance patterns. Over time, researchers recognized the mouse’s remarkable adaptability and suitability for investigating a broad spectrum of biological processes.
Advantages of Mice in Animal Research
- Small size: Mice are compact, which makes them less expensive to house and care for than larger animals.
- Rapid reproduction: Mice reach sexual maturity in just a few weeks and can produce litters of up to 10 pups, enabling researchers to generate large colonies for genetic studies.
- Short generational turnover: The rapid reproductive cycle of mice allows for multiple generations to be studied within a relatively short period, facilitating long-term experiments.
- Genetic malleability: Mice have a highly manipulable genome, which allows researchers to create genetically modified models to study specific genes or diseases.
- Well-characterized physiology: Extensive research on mice has generated a wealth of knowledge about their anatomy, metabolism, and behavior, making them a well-established model.
Contributions to Medical Advancements
Lab mice have played a pivotal role in numerous breakthroughs that have shaped modern medicine. Their contributions range from:
- Drug development: Mice are essential for testing the safety and efficacy of potential drugs prior to clinical trials.
- Immunology research: Mice have provided insights into how the immune system develops and functions, leading to advancements in vaccine development and treatments for autoimmune diseases.
- Cancer biology: Mouse models have enabled researchers to study cancer progression and metastasis, opening avenues for the development of targeted therapies.
- Genetic disorders: Mice bred with specific genetic mutations have helped identify the underlying causes of human diseases.
- Behavior and neuroscience: Mice have been invaluable for studying brain function and psychiatric disorders, including depression and anxiety.
Ethical Considerations
While mice have significantly contributed to scientific advancements, their use in animal research raises ethical concerns. It is essential to ensure that animal welfare is prioritized and that research is conducted responsibly. Ethical guidelines and regulations ensure the proper and humane care of laboratory animals, minimizing any discomfort or distress.
Conclusion:
Lab mice are true trailblazers in the world of animal research. Their unique characteristics and adaptability make them an ideal model organism for a wide range of scientific investigations. From the development of life-saving medications to unraveling the complexities of human diseases, mice have played an indispensable role in advancing medical knowledge and improving human health. As research continues, these unsung heroes will undoubtedly continue to contribute to uncovering new frontiers in medicine and biology.
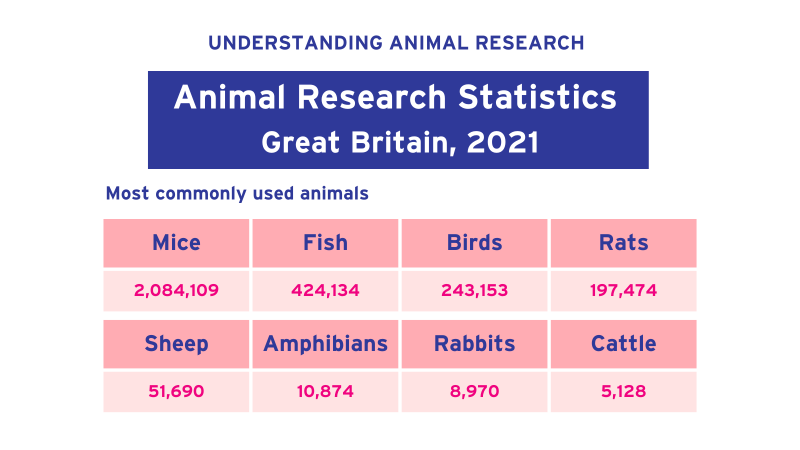
Image: uaroceania.org
________ Are The Most Commonly Used Species For Animal Research.

